What Is The Bronsted Lowry Definition Of A Base
What Is The Bronsted Lowry Definition Of A Base. So is nh3 an acid or base?. B a producer of hydrogen ions.
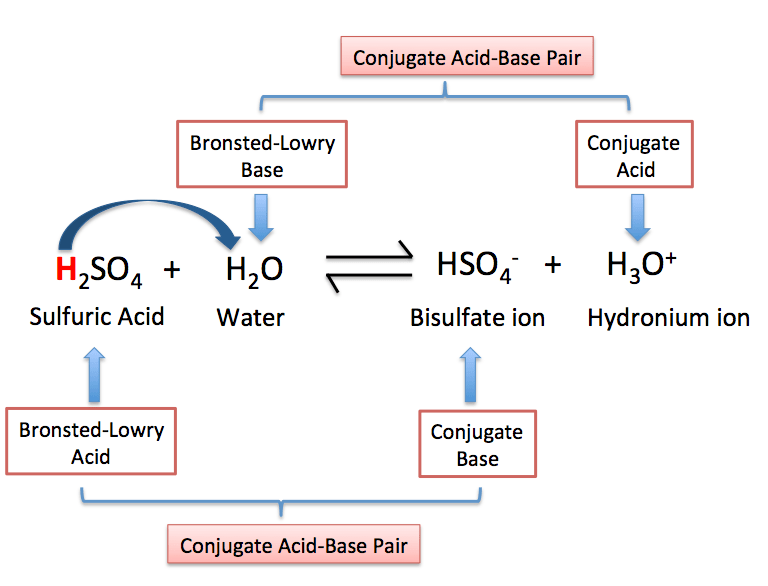
Have you ever head of the bronsted lowry theory of acids and bases, an essential theory of chemistry? A hydrogen ion is commonly referred to as a proton, and so acids and bases are. E a producer of hydroxide ions.
A Hydrogen Ion Is Commonly Referred To As A Proton, And So Acids And Bases Are.
For example, ammonia acts as a base when reacting with water to form a hydroxide ion and an. Tap card to see definition 👆. The solution that behaves as a proton donor is.
E A Producer Of Hydroxide Ions.
An example of a proton acceptor is ammonia (nh 3 ). A base is a substance that can accept protons or donate a pair of valence electrons to form a bond. The ammonia is happy to.
D A Substance That Dissolves In Water.
What is the ph of a 0.025 m solution of hclo 4? Have you ever head of the bronsted lowry theory of acids and bases, an essential theory of chemistry? So is nh3 an acid or base?.
(2) It Cannot Explain The Reactions Between.
The arrhenius definition of acids and bases is somewhat limited. Bases can be thought of as the chemical opposite of acids. According to the lewis definition, acids are molecules or ions capable of.
B A Producer Of Hydrogen Ions.
When a proton ( h+) accepts electrons donated from a lewis base (like oh− ), it exceeds its. Medium open in app solution verified by. It helps you fill the gaps in the arrhenius theory.
Post a Comment for "What Is The Bronsted Lowry Definition Of A Base"